- C uses
chartype to store characters and letters. - However, the
chartype is integer type because underneath C stores integer numbers instead of characters.
To represent characters, the computer has to map each integer with a corresponding character using a numerical code. The most common numerical code is ASCII, which stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
The following table illustrates the ASCII code:
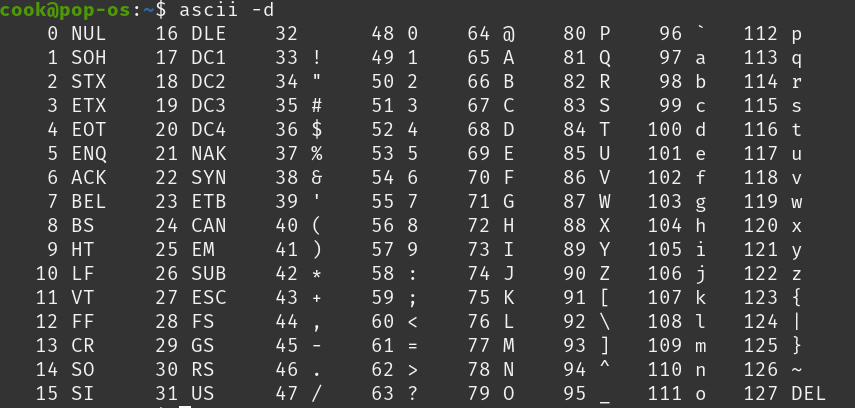
For example, the integer number 65 represents a character A in upper case.
Nota:
In C, the char type has a 1-byte unit of memory so it is more than enough to hold the ASCII codes. Besides ASCII code, there are various numerical codes available such as extended ASCII codes. Unfortunately, many character sets have more than 127 even 255 values. Therefore, to fulfill those needs, Unicode was created to represent various available character sets. Unicode currently has over 40,000 characters.