If
you can use these C Comparison Operators and C Logical Operators to perform different actions for different decisions.
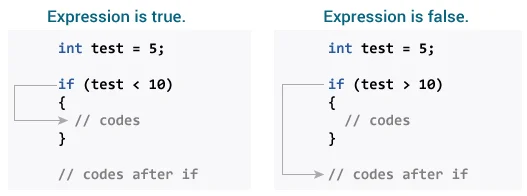
If Syntax
The syntax of the if statement in C programming is:
if (test expression)
{
// code
}How if statement works?
The if statement evaluates the test expression inside the parenthesis ().
- If the test expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body of
ifare executed. - If the test expression is evaluated to false, statements inside the body of
ifare not executed.
If … Else
Use the else statement to specify a block of code to be executed if the condition is false.
If … Else Syntax
if (test expression) {
// run code if test expression is true
}
else {
// run code if test expression is false
}How if…else statement works?
If the test expression is evaluated to true:
- statements inside the body of
ifare executed - statements inside the body of
elseare skipped from execution
If the test expression is evaluated to false:
- statements inside the body of
ifare skipped from execution - statements inside the body of
elseare executed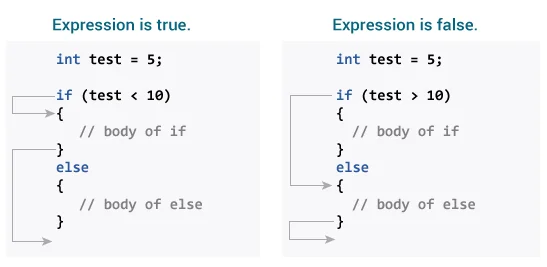
If…else Ladder (else if)
Use the else if statement to specify a new condition if the first condition is false.
else if Syntax
f (test expression1) {
// statement(s)
}
else if(test expression2) {
// statement(s)
}
else if (test expression3) {
// statement(s)
}
.
.
else {
// statement(s)
}Short Hand If…Else (Ternary Operator)
- There is also a short-hand if else, which is known as the ternary operator because it consists of three operands.
- It can be used to replace multiple lines of code with a single line. It is often used to replace simple if else statements
Syntax
variable_= (condition) ? expressionTrue : expressionFalse;Example
int time = 20;
(time < 18) ? printf("Good day.") : printf("Good evening.");Kiketta
Warning
If the body of an
if...elsestatement has only one statement, you do not need to use brackets{}.
For example, this code:
if (a > b) {
printf("Hello");
}
printf("Hi");is equivalent to:
if (a > b)
printf("Hello");
printf("Hi");