A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable as its value.
How to declare a pointer
int* p0;
int *p1;
int * p2;Stranger case:
int* p1, p2;Here, we have declared a pointer p1 and a normal variable p2.
Assigning addresses to Pointers
Let’s take an example.
int* pc, c;
c = 5;
pc = &c;Here, 5 is assigned to the c variable. And, the address of c is assigned to the pc pointer.
Get Value of Thing Pointed by Pointers
To get the value of the thing pointed by the pointers, we use the * operator.
int* pc, c;
c = 5;
pc = &c;
printf("%d", *pc); // Output: 5Warning
Note: In the above example, pc is a pointer, not
*pc. You cannot do something like*pc = &c;By the way,
*is called the dereference operator (when working with pointers). It operates on a pointer and gives the value stored in that pointer.
Changing Value Pointed by Pointers
int* pc, c;
c = 5;
pc = &c;
*pc = 1;
printf("%d", *pc); // Ouptut: 1
printf("%d", c); // Output: 1- We have assigned the address of c to the pc pointer.
- Then, we changed
*pcto 1 using*pc = 1;. Since pc and the address of c is the same, c will be equal to 1.
Let’s take one more example:
int* pc, c, d;
c = 5;
d = -15;
pc = &c; printf("%d", *pc); // Output: 5
pc = &d; printf("%d", *pc); // Ouptut: -15- Initially, the address of c is assigned to the pc pointer using
pc = &c;. Since c is 5,*pcgives us 5. - Then, the address of d is assigned to the pc pointer using
pc = &d;. Since d is -15,*pcgives us -15.
Common Mistakes
Suppose, you want pointer pc to point to the address of c.
int c, *pc;
// pc is address but c is not
pc = c; // Error
// &c is address but *pc is not
*pc = &c; // Error
// both &c and pc are addresses
pc = &c; // Not an error
// both c and *pc are values
*pc = c; // Not an errorHere’s an example of pointer syntax beginners often find confusing.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int c = 5;
int *p = &c;
printf("%d", *p); // 5
return 0;
}Why didn’t we get an error when using int *p = &c;?
It’s because
int *p = &c;is equivalent to
int *p:
p = &c;In both cases, we are creating a pointer p (not *p) and assigning &c to it.
To avoid this confusion, we can use the statement like this:
int* p = &c;Long Example: Working of Pointers
Let’s take a working example.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int* pc, c;
c = 22;
printf("Address of c: %p\n", &c);
printf("Value of c: %d\n\n", c); // 22
pc = &c;
printf("Address of pointer pc: %p\n", pc);
printf("Content of pointer pc: %d\n\n", *pc); // 22
c = 11;
printf("Address of pointer pc: %p\n", pc);
printf("Content of pointer pc: %d\n\n", *pc); // 11
*pc = 2;
printf("Address of c: %p\n", &c);
printf("Value of c: %d\n\n", c); // 2
return 0;
}Output
Address of c: 2686784 Value of c: 22
Address of pointer pc: 2686784 Content of pointer pc: 22
Address of pointer pc: 2686784 Content of pointer pc: 11
Address of c: 2686784 Value of c: 2
Explanation of the program
-
int* pc, c;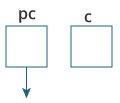
Here, a pointer pc and a normal variable c, both of type
int, is created.
Since pc and c are not initialized at initially, pointer pc points to either no address or a random address. And, variable c has an address but contains random garbage value.
-
c = 22;
This assigns 22 to the variable c. That is, 22 is stored in the memory location of variable c.
-
pc = &c;
This assigns the address of variable c to the pointer pc.
-
c = 11;
This assigns 11 to variable c.
-
*pc = 2;
This change the value at the memory location pointed by the pointer pc to 2.