In programming, a loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is met.
For Loop
When you know exactly how many times you want to loop through a block of code, use the for loop instead of a C While Loops
Syntax
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement)
{
// statements inside the body of loop
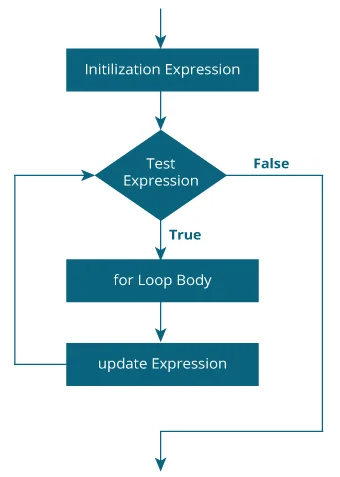
}How for loop works?
- The initialization statement is executed only once.
- Then, the test expression is evaluated. If the test expression is evaluated to false, the
forloop is terminated. - However, if the test expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body of the
forloop are executed, and the update expression is updated. - Again the test expression is evaluated.
This process goes on until the test expression is false
Note: testExpression it’s made by C Comparison Operators and C Logical Operators.
For loop Flowchart
Example 1:
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i;
for (i = 1; i < 11; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}Output: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Example 2:
// Program to calculate the sum of first n natural numbers
// Positive integers 1,2,3...n are known as natural numbers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num, count, sum = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
// for loop terminates when num is less than count
for(count = 1; count <= num; ++count)
{
sum += count;
}
printf("Sum = %d", sum);
return 0;
}Oputput: Sum = 55