In programming, a loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is met.
While Loops
The while loops through a block of code as long as a specified condition is true:
Syntax
while (condition) {
// code block to be executed
}How while loop works?
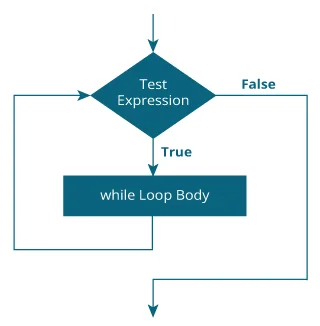
- The
whileloop evaluates thetestExpressioninside the parentheses(). - If
testExpressionis true, statements inside the body ofwhileloop are executed. Then,testExpressionis evaluated again. - The process goes on until
testExpressionis evaluated to false. - If
testExpressionis false, the loop terminates (ends).
Note: testExpression it’s made by C Comparison Operators and C Logical Operators.
For loop Flowchart
Example:
// Print numbers from 1 to 5
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
printf("%d\n", i);
++i;
}
return 0;
}Output: 1 2 3 4 5
Do…While Loop
The body of do...while loop is executed at least once.
Only then, the test expression is evaluated.
Syntax
do {
// the body of the loop
}
while (testExpression);How do…while loop works?
- The body of
do...whileloop is executed once. Only then, thetestExpressionis evaluated. - If
testExpressionis true, the body of the loop is executed again andtestExpressionis evaluated once more. - This process goes on until
testExpressionbecomes false. - If
testExpressionis false, the loop ends.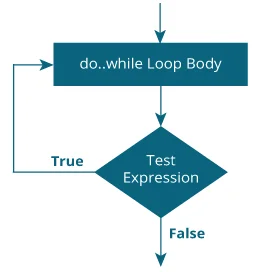
Example:
// Program to add numbers until the user enters zero
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
double number, sum = 0;
// the body of the loop is executed at least once
do {
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &number);
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0.0);
printf("Sum = %.2lf",sum);
return 0;
}Output:
Enter a number: 1.5
Enter a number: 2.4
Enter a number: -3.4
Enter a number: 4.2
Enter a number: 0
Sum = 4.70