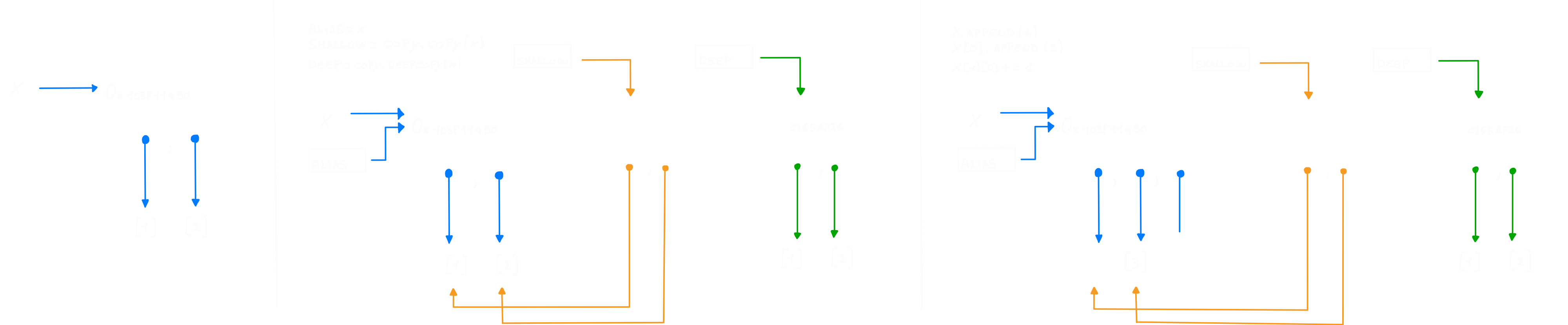
Index
- Alias
- Shallow copy vs Deep copy
- Shallow copy vs Deep copy (unmutable objects)
- Shallow copy vs Deep copy (mutable objects)
Alias
- The assignment operator in python:
- Doesn’t create a copy of the objects
- It makes bindings between a variable and a object
Partial example:
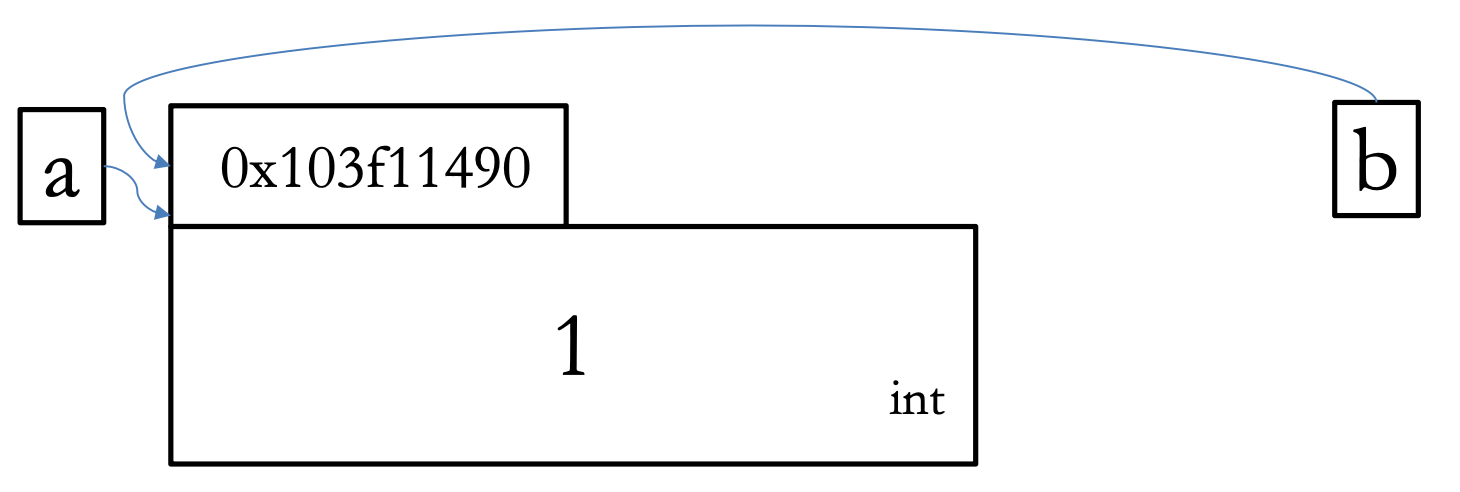
a = [1,2,3]
b = a # y is an alias of x
a.append(4)
#a.out = [1,2,3,4]
#b.out = [1,2,3,4]
print(a is b) #Output: True
a = 1
#a.out = 1
#b.out = [1,2,3,4]
print(a is b) #Output: False
Shallow copy vs Deep copy
Shallow copy: Create a new object and insert references into the new object pointed at those found in the original.
Deep copy: Create a new object, and then recursively insert redundant copies of the objects found in the original.
Shallow copy vs Deep copy (unmutable objects)
Oss:
There isn’t any difference between alice, shallow copy and deep copy of an unmutable object
Unmutable not compound object
import copy
x = "hello world"
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
#test is x?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: True
print(deep is x) #Output: True
# x edit test
x += '!' # you can't modify an unmutable object,
# so the new x is a different object than the old x
print(alias is x) #Output: False
print(shallow is x) #Output: False
print(deep is x) #Output: False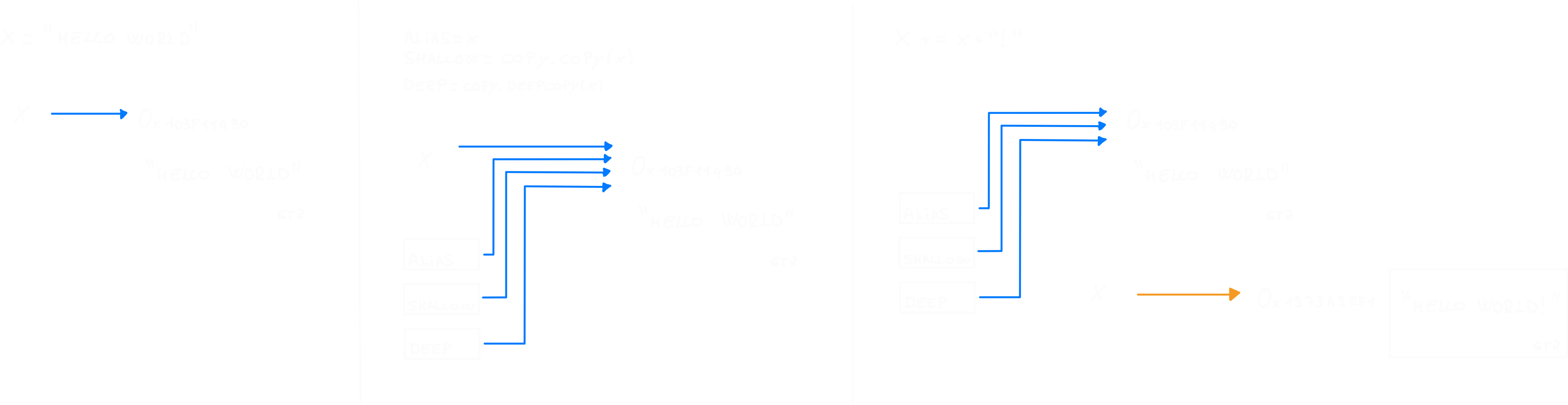
Unmutable object compound by unmutable objects
import copy
x = ((1), 2)
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
#test is X?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: True
print(deep is x) #Output: True
# x[1] += 1 -> error
#you can't use an assignment operator on a tuple item
#so it's impossible to edit it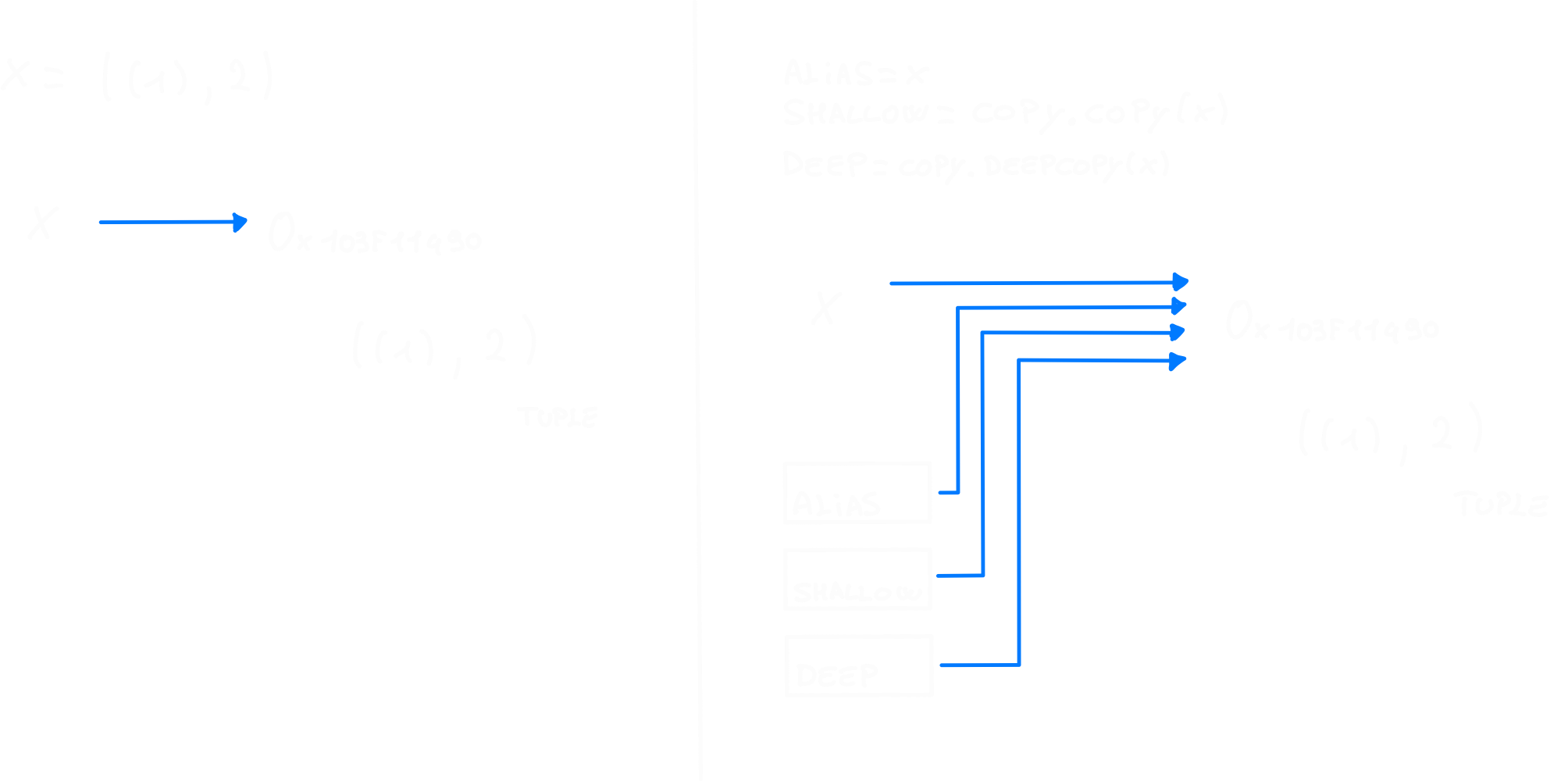
Unmutable object compound by un mutable objects:
import copy
x = ([1], {3})
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
#test is x?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: True
print(deep is x) #Output: False
# test is x[0]
print(alias[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(shallow[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(deep[0] is x[0]) #Output: False
#x item edit tedt
x[0].append(2),
print(alias) #Output: ([1, 2], {3})
print(shallow) #Output: ([1, 2], {3})
print(deep) #Output: ([1], {3})
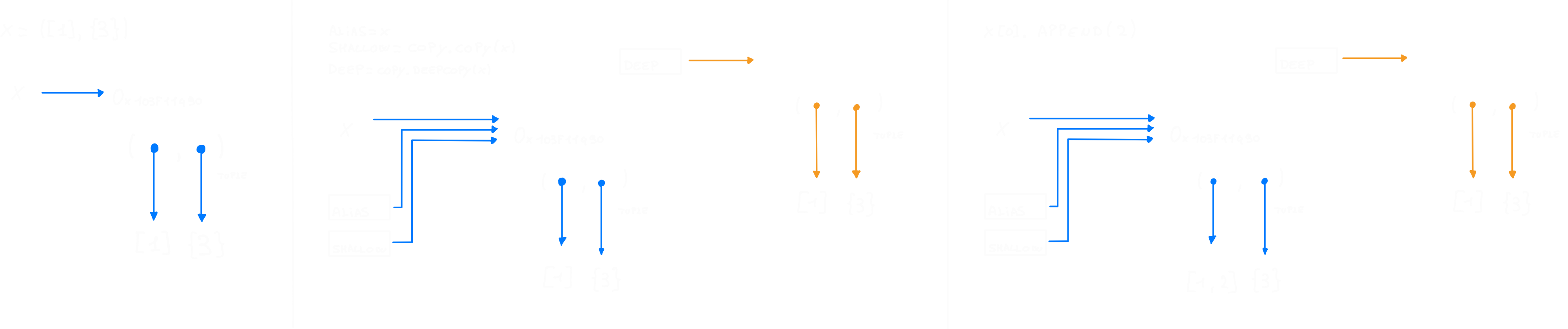
Shallow copy vs Deep copy (mutable objects)
Mutable not compound object
import copy
x = [1,1]
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
# test is x?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: False
print(deep is x) #Output: False
# test is x[1]
print(alias[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
print(shallow[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
print(deep[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
# x edit test
x.append(3)
print(alias) #Output: [1,1,3]
print(shallow) #Output: [1,1]
print(deep) #Output: [1,1]
# x item edit test
x[1] += 1
print(alias) #Output: [1,2,3]
print(shallow) #Output: [1,1]
print(deep) #Output: [1,1]
# test is x[1]
print(alias[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
print(shallow[1] is x[1]) #Output: False
print(deep[1] is x[1]) #Output: False
Mutable object compound by unmutable objects
import copy
x = ["hello", 1]
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
# test is x ?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: False
print(deep is x) #Output: False
# test is x[0]
print(alias[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(shallow[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(deep[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
# test is x[1]
print(alias[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
print(shallow[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
print(deep[1] is x[1]) #Output: True
# x item edit test
x[0] += "!" # you cant't edit a string so the result is a new sting
print(alias) #Output: ['hello!', 1]
print(shallow) #Output: ['hello', 1]
print(deep) #Output: ['hello', 1]
# test is x[0]
print(alias[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(shallow[0] is x[0]) #Output: False
print(deep[0] is x[0]) #Output: False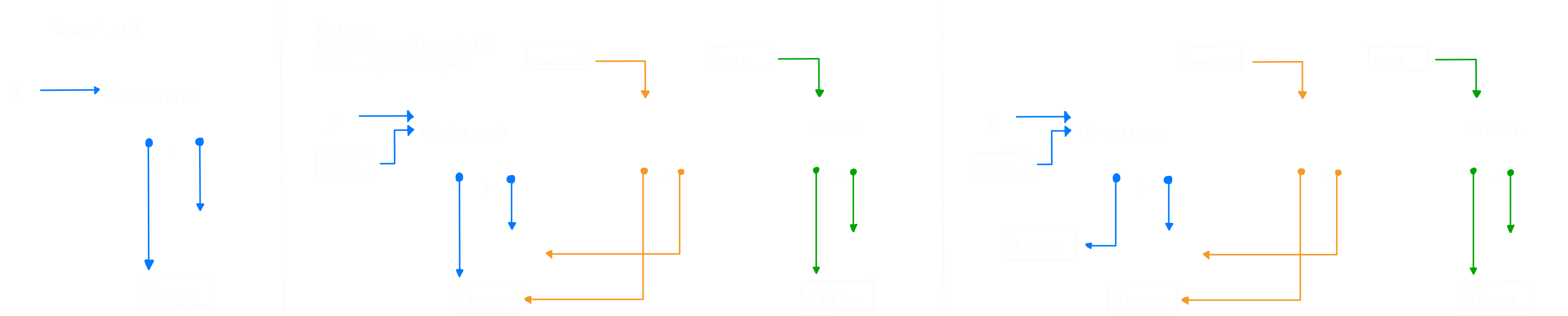
Mutable object compound by un mutable objects
import copy
x = [[1], [2]]
alias = x
shallow = copy.copy(x)
deep = copy.deepcopy(x)
# test is x ?
print(alias is x) #Output: True
print(shallow is x) #Output: False
print(deep is x) #Output: False
# test is x[0]
print(alias[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(shallow[0] is x[0]) #Output: True
print(deep[0] is x[0]) #Output: False
# x edit test
x.append(4)
x[0].append(2)
x[1][0] += 1
print(alias) #Output: [[1, 2], [3], 4]
print(shallow) #Output: [[1, 2], [3]]
print(deep) #Output: [[1], [2]]