Index
UML Class Notation
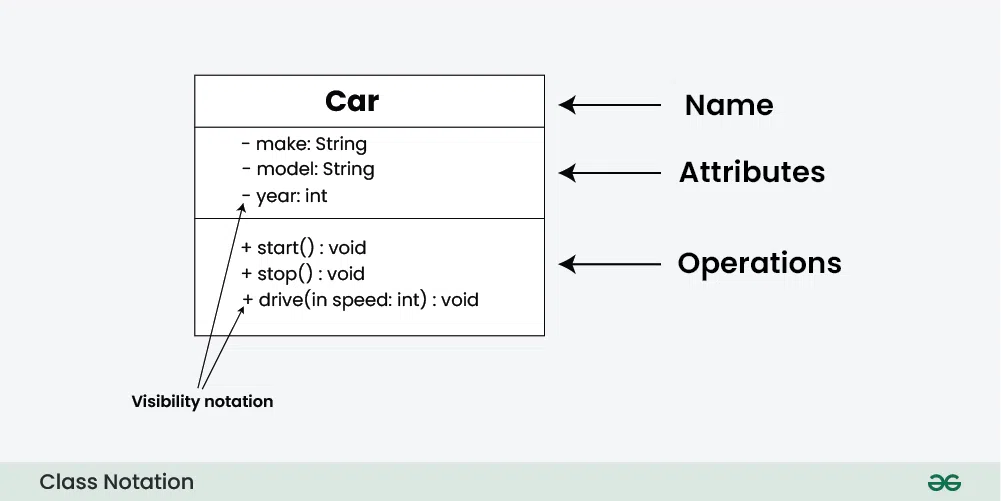
The UML Class diagram is a graphical notation used to construct and visualise object oriented systems by showing the system’s:
-
Class Name:
- The name of the class is typically written in the top compartment of the class box and is centred and bold.
-
- Attributes, also known as properties or fields, represent the data members of the class.
- They are listed in the second compartment of the class box and often include the visibility (e.g. public, private) and the data type of each attribute.
-
- Methods, also known as functions or operations, represent the behaviour or functionality of the class.
- They are listed in the third compartment of the class box and include the visibility (e.g., public, private), return type, and parameters of each method.
Attributes
In UML Class Diagram notation visibility fieldName : dataType <static> <final> is a way to represent the fields of a class.
Here’s what each part means:
-
visibility: This indicates the visibility of the attribute. It can be public (+), private (-), protected (#), or package (~).- read Visibility Notation for more information
-
fieldName: This is the name of the field. -
dataType: This is the type of the attribute (e.g., int, String, etc.). -
<static>: If present, this indicates that the attribute is static. -
<final>: If present, this indicates that the attribute is final.
For example, - count : int <static> <final> would represent a private, static, final attribute named count of type int.
Tip
Read about Java Fields to lear more
Methods
In UML Class Diagram notation, methods are represented visibility methodName(parameters) : returnType <static> <abstract>
Here’s what each part means:
-
visibility: This indicates the visibility of the method. It can be public (+), private (-), protected (#), or package (~).- read Visibility Notation for more information
-
methodName: This is the name of the method. -
parameters: These are the input parameters for the method. Each parameter includes a name and a type, separated by a colon, and multiple parameters are separated by commas. -
returnType: This is the type of value that the method returns. -
<static>: If present, this indicates that the method is static. In UML, static methods are usually underlined.
For example, + calculateSum(a: int, b: int) : int <static> would represent a public, static method named calculateSum that takes two parameters of type int and returns an int.
Tip
Read about Java Methods to learn more
Visibility Notation
Visibility notations indicate the access level of attributes and methods. Common visibility notations include:
+for public (visible to all classes)-for private (visible only within the class)#for protected (visible to subclasses)~for package or default visibility (visible to classes in the same package)
Tip
Read Java Access Modifier to learn more
Classes Dependance
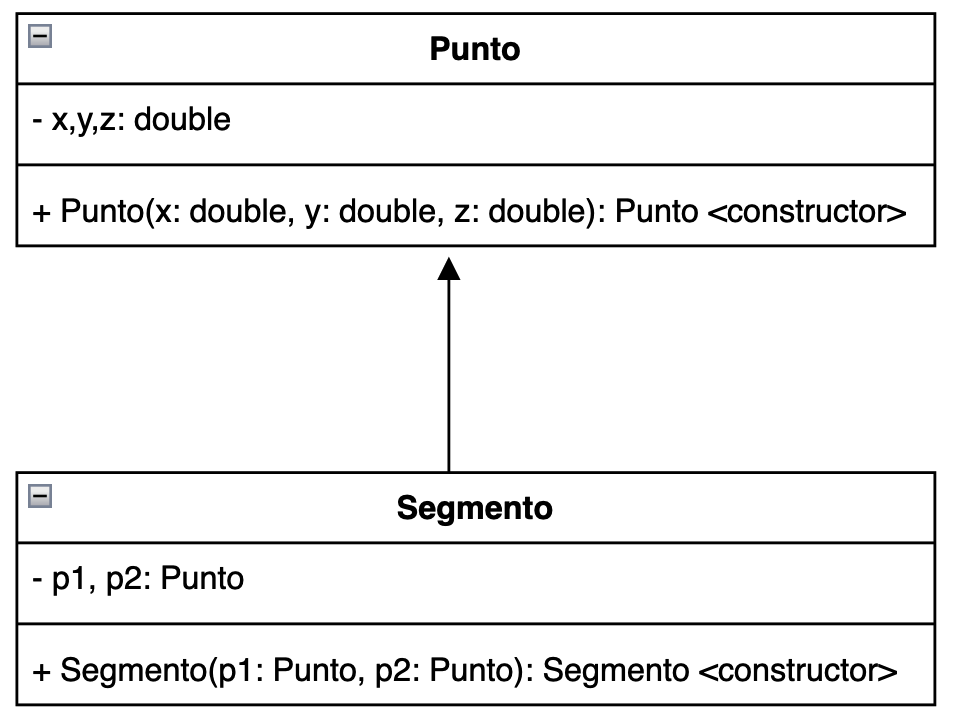
Posso utilizzare la freccia piena in modo tale da indicare la dipendenza generica tra due classi.